On December 17, 2024, Ethiopia’s parliament passed legislation enabling foreign banks to enter Ethiopia’s hitherto closed financial sector. The legislation, known as the Banking Business Proclamation, permits foreign banks to establish subsidiaries, open branches or representative offices, and acquire stakes in local banks.
The liberalization of the financial sector — which includes the operationalization of a stock market — is part of the Abiy Ahmed regime’s ongoing effort to liberalize and privatize the commanding heights of the Ethiopian economy.
Under its so-called Homegrown Economic Reform Agenda — overseen and funded by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and Word Bank — the Abiy regime has adopted a slew of precarious economic policies that have shifted Ethiopia’s economy away from the developmental state model that prioritized manufacturing and a strategic industrial policy in favor of neoliberalism.
In so doing, expediting the liberalization of the economy and privatization of the commanding heights; while at the same time, allocating limited foreign exchange earnings toward tourism and mining — largely underperforming sectors.
Currently, the Abiy regime’s agenda to liberalize and privatize the commanding heights of the economy extends to telecom, banking, power, logistics, and transportation. There have also been discussions about selling shares of Ethiopian Airlines — the country’s most profitable state-owned enterprise. Moreover, as a consequence of a new IMF structural adjustment program signed in July 2024, the Abiy regime liberalized the exchange rate and floated the Ethiopian Birr — leading to a 120% depreciation of the currency, increasing poverty, and precipitating a cost-of-living crisis. Simultaneously, in recent months, the banking, retail, and real estate sectors have all been liberalized.
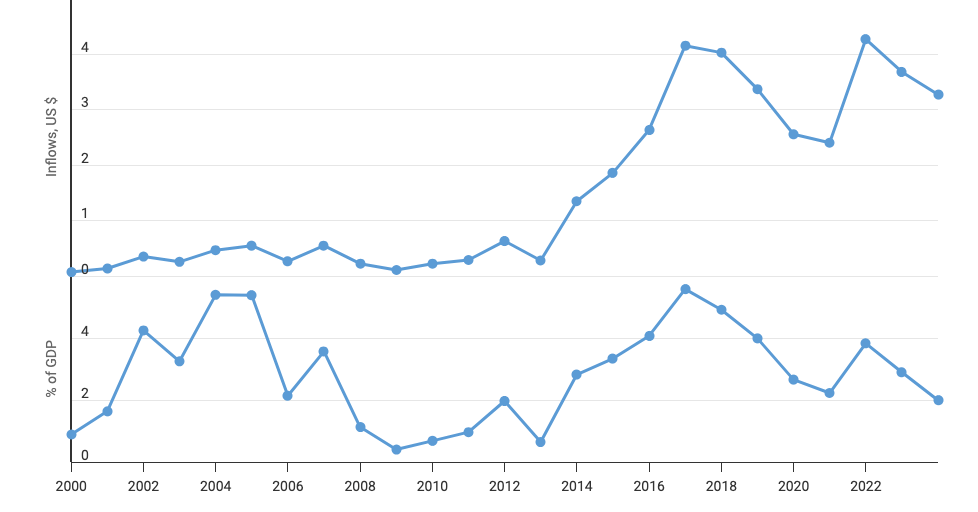
Liberalization and privatization are driven by the need to attract foreign direct investment (FDI). Since Abiy assumed power in 2018 — due to economic mismanagement, proliferation of armed conflict, and Ethiopia’s removal from AGOA — FDI inflows have drastically declined, both in absolute amount and as a % of GDP (Figure 1) — driven by the precipitous decline in manufacturing FDI inflows. Notably, the anomalous uptick in FDI inflows in 2021-22 was due to the selling of a telecom license to Safaricom as part of the ongoing liberalization and privatisation agenda.
Comparatively, between 2013-17, as a consequence of a well formulated industrial parks program launched in 2012, FDI inflows increased consistently. For instance, in 2016-17, FDI inflow was $4.2 billion of which $3.7 billion was manufacturing FDI. Similarly, manufacturing value-added increased from $1.5 billion in 2012 to $5 billion in 2017.
Figure 1: Foreign Direct Investment, Net Inflows (US$ Billions and % of GDP) (2000-23)
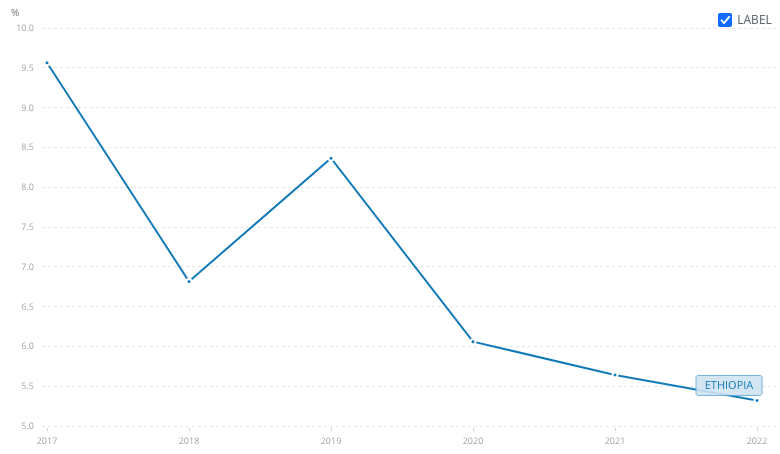
Since Abiy assumed power, economic growth has also declined significantly — down from 9.6% to 5.3% (Figure 2).
Figure 2: GDP Growth (Annual %) (2017-22)
Perhaps more jarring than the wholesale privatization and liberalization agenda, is the manner of policy implementation. Neoliberal economic policies are being implemented through shock therapy in “one big bang.” As the experiences of Russia and Eastern European countries illustrate, shock therapy leads to inflation, wage-price spirals, austerity measures, de-industrialization, corruption, and increasing levels of poverty and inequality. All of which currently afflict Ethiopia.
Government Obfuscation
While the Abiy regime’s wholesale adoption of neoliberalism is clear, officials are sending mixed signals. In a recent interview with African Business, Brook Taye, chief executive of government-owned Ethiopian Investment Holdings, said: “Liberalising the market does not mean selling off state assets. The government does not have a privatisation strategy: what we have is a state-owned enterprise reform strategy.”
Not only is the statement factually inaccurate, but it also contradicts the official economic policy objectives of the Abiy regime as delineated in the so-called “Homegrown Economic Reform Agenda: A Pathway to Prosperity.”
According to the official document, the regime aims to “strengthen public finances including through improving the efficiency of state-owned enterprises and privatisation.”
Similarly, according to the “Ten Year Development Plan: A Pathway to Prosperity,” a principle objective of the Ten Year Development plan is: “expediting the privatisation of large state-owned enterprises and liberalisation of priority sectors.”
In other words, liberalisation and privatisation of the economy, including state-owned enterprises through shock therapy: a policy approach that aligns with the prescriptions of international financial institutions which are overseeing and financing the Abiy regime’s economic policy, in particular the so-called “reform agenda”.
Obfuscation by regime officials will only serve to demonstrate incompetence and sow confusion, while undermining the policy certainty essential for reassuring the private sector and attracting foreign investment.
Gradual and Sequenced Market-Oriented Reforms are Needed
Unlike the shock therapy approach of the Abiy regime, gradual and sequenced market-oriented reforms would best serve the Ethiopian economy. Gradual and sequenced reforms would ensure the competitiveness of local firms against foreign competition, while safeguarding against challenges, including regulatory complexities; destabilisation of the banking, retail, and real estate sectors; and ultimately, the risks associated with market volatility and financial contagion. Gradual and sequenced market-oriented reform is a key lesson of the Chinese development experience and the East Asian Miracle, the rapid economic growth of eight East Asian countries between 1965 and 1990.
At the same time, the economic priority must be attracting FDI toward the country’s dynamic comparative advantage with the principal aim of facilitating structural transformation by bolstering manufacturing productivity and industrial capacity, generating employment, and increasing wages. This must be coupled with improving human capital, technology acquisition, and bolstering linkages between foreign and domestic firms. This is being completely neglected in favour of vanity projects in the tourism sector, including the construction of resorts, lodges, and palaces.
Unfortunately, rather than developing the Ethiopian economy, Abiy is intent on selling off state assets, while “developing corridors” through unproductive vanity projects, including the installation of decorative lighting, bike lanes, and water fountains.
Editors Note: A version of this article was published by Africa Business on January 7, 2025.




